Spherical Cast Tungsten Carbide Powder is a novel type of highly wear-resistant ceramic particle material. Compared to traditional tungsten carbide, spherical cast tungsten carbide possesses two significant advantages. Firstly, it has a regular spherical appearance with good powder flowability and wetting properties. When used as an additive particle, it exhibits excellent compatibility with the surrounding structure, reducing stress concentration. Secondly, the internal structure of the tungsten carbide particles is dense, exhibiting good toughness, fine grain size, high hardness, and excellent wear resistance as a coating. It is less prone to fracture under load.
Due to its outstanding performance, spherical cast tungsten carbide powder is gradually replacing traditional tungsten carbide powder in surface protection applications for mining machinery, petroleum machinery, construction industry, and foundries. It significantly enhances the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance of components, thereby extending their service life.
The chemical composition, microscopic morphology, microstructure, microhardness, and other powder properties of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by different methods will be investigated below.
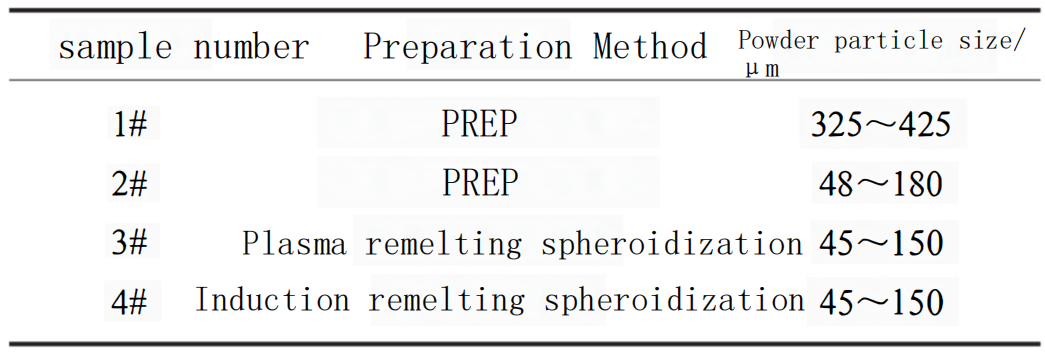
1.Chemical composition of sample carbide powder
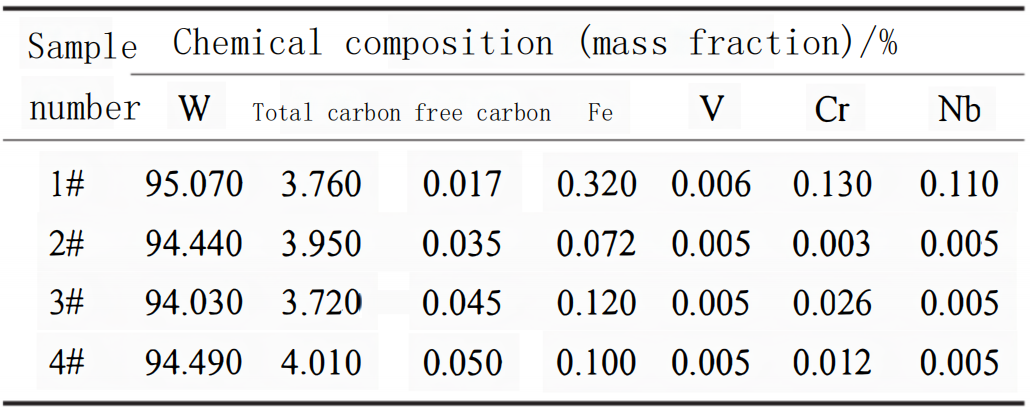
The table above shows the chemical composition of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder samples prepared by different methods. It can be observed that the main components of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder are tungsten (W) and carbon (C), with trace amounts of iron (Fe), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), and niobium (Nb). The ideal composition of spherical cast tungsten carbide should consist of eutectic WC and W2C phases, with a eutectic temperature of 2525 ℃ and a carbon content of 3.840% (mass fraction) at the eutectic point. From the data in the table, it can be seen that the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the smallest deviation from the theoretical carbon content and the lowest free carbon content. On the other hand, the powder obtained from the induction melting and atomization method shows the largest deviation from the theoretical carbon content, with a difference of 0.170% (mass fraction). This is likely due to the use of graphite tube heating in the induction melting process, which can increase the carbon content. Therefore, compared to other methods, the plasma rotating electrode atomization method can more accurately control the carbon content of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder, preventing over-eutectic and sub-eutectic reactions caused by carburization and decarburization, and achieving a near-perfect eutectic microstructure. This is crucial for improving the microstructure and properties of spherical cast tungsten carbide.
2.Microscopic morphology

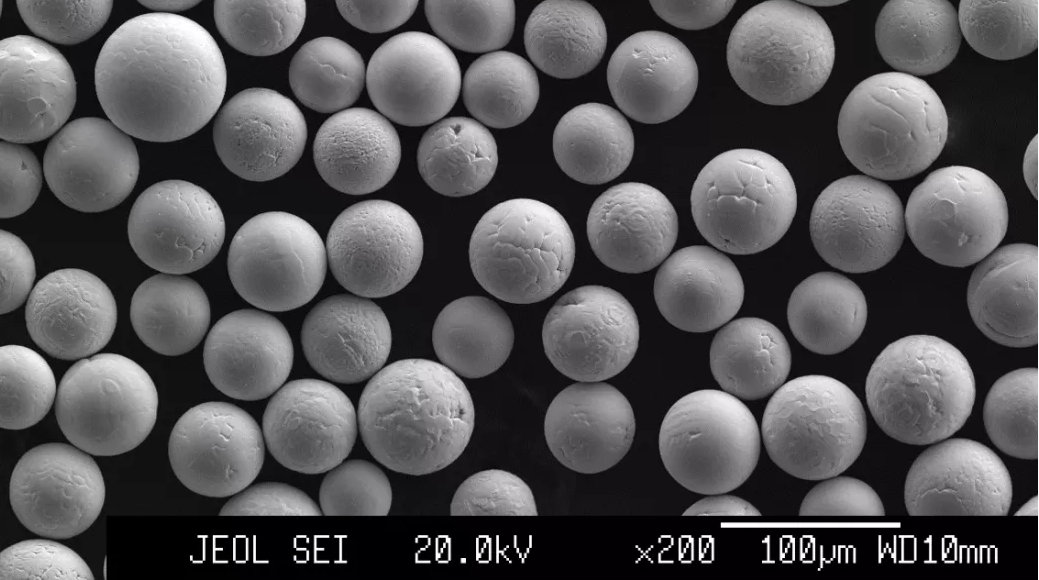
The figure above shows the microstructure of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by different methods. It can be observed that the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder obtained from all three methods exhibits a regular and smooth near-spherical shape.

The figure above shows cross-sectional photographs of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by different methods. From (a) and (b), it can be observed that the particles of spherical tungsten carbide powder prepared by plasma rotating electrode atomization method have a dense internal structure with almost no defects. However, from (c) and (d), it can be seen that spherical tungsten carbide powder prepared by plasma melting and atomization as well as induction melting and atomization methods have some noticeable pores or hollow particles within their internal structure. The main reason for this is that the crushed tungsten carbide powder used as raw material in the above-mentioned methods may contain residual pores from the casting process. During the short-duration plasma or induction heating process, it becomes challenging for the internal part of the crushed tungsten carbide powder to fully melt, resulting in the presence of some pores within the particles.
3.Microstructure

The figure above displays microscopic images of the microstructure of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by different methods after corrosion. It can be observed that the internal structure of the particles in all three methods primarily consists of a typical fine needle-like eutectic structure of WC and W2C phases. Compared to plasma melting and atomization and induction melting and atomization methods, the eutectic microstructure of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder obtained by plasma rotating electrode atomization method appears to be finer and denser. This is because, in contrast to plasma melting and atomization and induction melting and atomization methods, plasma rotating electrode atomization method fully melts the tungsten carbide raw material rod and rapidly solidifies it under the centrifugal force. The higher undercooling during the crystallization of the molten tungsten carbide results in more rapid nucleation and a greater number of crystal nuclei formation, leading to a finer eutectic microstructure.
4.Microhardness
The table below shows the average microhardness of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by different methods. It can be observed that the microhardness of the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder obtained from all three methods is above 2800 HV0.1. Among them, the powder produced by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method exhibits the highest microhardness, reaching 3045 HV0.1. This is mainly due to the finer and denser eutectic microstructure within the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder obtained by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method.

5.Other physical properties
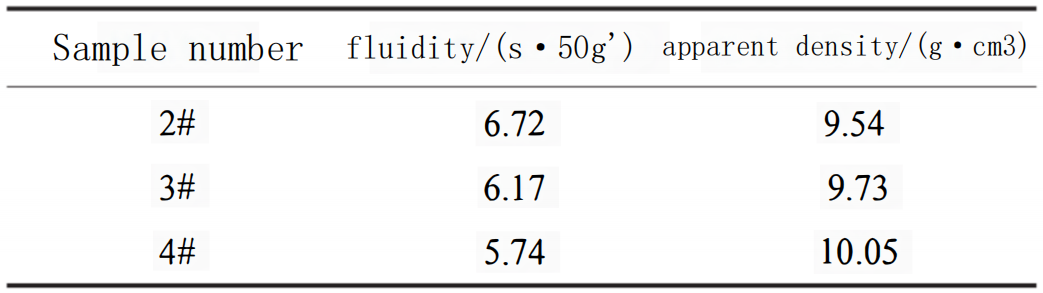
The table below presents the flowability and tap density values of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by different methods. It can be observed that the powder obtained from the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the poorest flowability and the lowest tap density. On the other hand, the powder obtained from the induction melting and atomization method exhibits the best flowability and the highest tap density.
??züm
(1) The spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method exhibits the smallest deviation from the theoretical carbon content and eutectic carbon content, with the lowest free carbon content and relatively low impurity content.
(2) The internal structure of the spherical tungsten carbide powder particles obtained by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method is dense, with almost no defects. The eutectic microstructure is finer and denser. On the other hand, the particles obtained by plasma melting and atomization as well as induction melting and atomization methods show some noticeable pores or hollow particles within their internal structure.
(3) All three methods result in spherical cast tungsten carbide powder primarily consisting of WC and W2C phases.
(4) The microhardness of the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder obtained by all three methods is above 2800 HV0.1. Among them, the powder produced by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method exhibits the highest microhardness, reaching 3045 HV0.1. The powder obtained by the induction melting and atomization method shows good flowability and the highest tap density.

Hello. I work in the aviation sector and we are metal strip drawing SS aviation grade metal and cannot seem to find a carbide that gives us the toughness and long wear properties that normal carbide would provide with regular tungsten carbide used in metal drawing of softer materials?Would you have a supplier list of companies that provide this new type of carbide? Regards
Hello Dale,
Thank you for leaving a comment!
Could you please send us an inquiry to [email protected]?
Sayg?lar?mla,