The so-called powder metallurgy method is to make a powder of the raw material of the alloy to be produced, and then mix the powders in an appropriate amount and pressurize and solidify into a certain shape. These powder pieces will be placed in a reducing atmosphere (for example, hydrogen), heated and sintered to form an alloy. This is a metallurgical method that is completely different from the previous casting method.
The sintering referred to herein can be simply defined as the promotion of agglomeration of metal crystal grains by the action of pressurization and warming. We apply a certain amount of pressure to the powder with the alloy composition to compact it. At high temperatures, the intimately contacted powders stick to each other and gradually fill the voids to form a high density alloy. The heating temperature at this time is the melting temperature of the low melting component in the alloy component. Thus, the alloy ingot is sintered at a temperature below the melting point of the entire powder component. This method is similar to the method of combining the two processes of smelting and casting, and its properties are close to those of cast alloys. But from a metallographic point of view, it should be a branch of alloy castings.
Cemented carbide is manufactured by this powder metallurgy method. Generally, powders such as tungsten, carbon, cobalt, titanium, and cerium are used for batch mixing, and then pressed and sintered to form an alloy. Thus, the product of this metallurgical process is also referred to as a sintered cemented carbide or a cemented carbide alloy. In recent years, powder metallurgy methods have developed very rapidly. Cemented carbides, oil-bearing alloys, electrical contacts, metal bonded diamond wheels, and special decorative metal products are all manufactured by this powder metallurgy method.
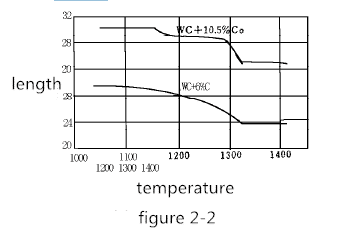
For example, the pressed semi-finished product of 30 mm in length is now heated to 1000-1400 ° C. The volume change of the pressed product at about 30 ° C for about 5 minutes is shown in Figure 2-2. Shrinkage generally begins at 1150 ° C. In the case of 6% Co, the shrinkage proceeds very regularly, ending at approximately 1320 ° C. In the case of 10% Co, at 1180-1200 ° C, the contraction is temporarily interrupted. As the temperature continues to rise, the shrinkage proceeds rapidly, and when the temperature reaches 1300 ° C, it tends to balance.
Thereafter, since the number of contact points of the particles and the contact area is remarkably increased, each of the particles is in a state of easily releasing excess energy (free energy) held by itself. Thus, from about 200 ° C, cobalt begins to diffuse, at which point the first stage of sintering begins. When the temperature rises again, β-Co is converted to γ-Co at around 490 °C. At 600 ° C, carbon begins to diffuse into the cobalt and becomes a mass solution. The finer the tungsten carbide particles, or the better the cobalt-coated tungsten carbide, the faster this diffusion phenomenon will occur. This diffusion has the same effect as applying strong compressive pressure to the compact. However, during the temperature rise, almost no liquid phase is observed at this temperature.
However, near this temperature, the bending strength is significantly increased. Usually, a hardness alloy of 6% cobalt is sintered at a temperature of about 1400 ° C. At this temperature, WC gradually dissolves into the liquid phase, and particularly fine WC dissolves rapidly, and the large WC has large surface energy due to the sharp corner portion. It is round after being dissolved. As a result, the liquid phase portion becomes more and more, and as the reaction progresses toward the direction in which the free energy decreases, the alloy shrinks and the pores gradually decrease. On the other hand, in the portion where the tungsten carbide particles are in contact with each other, the phenomenon of volume diffusion, particularly surface diffusion, continues to occur. There is also the possibility that carbide particles will bond with each other. Further, WC may also locally precipitate from the liquid phase at a portion where the tungsten carbide contacts each other. As a result, various reasons have prompted the growth of tungsten carbide grains, resulting in a dense alignment. However, the temperature is further increased, and when it exceeds 1600 ° C, gas is generated inside the product, causing expansion of the crystal arrangement. It is said that the gas is generated by the presence of impurities such as SiO2. On the contrary, if the temperature is lowered, the WC particles dissolved in the liquid phase are precipitated on the WC particles having small surface energy. Even after the liquid phase disappears into a solid state, the tungsten carbide continues to separate until only 1% remains.
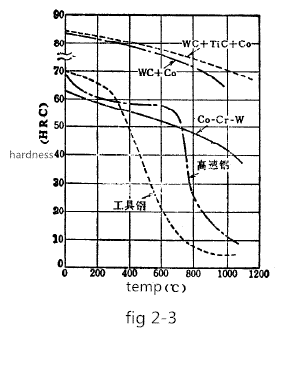
During the sintering process, the tungsten carbide present in the form of a melt in the cobalt moves a small distance and is bonded to the undissolved tungsten carbide, so that uneven structure such as a cast alloy is not formed. The steel containing a large amount of pearlite is aged and hardened by the precipitation of the carbon melt of the alpha iron. In contrast, during the sintering process, the WC particles act as effective nucleation, so there is no age hardening phenomenon, so that the structure is uniform and very stable, not sensitive to heat treatment, and the hardness does not change even at relatively high temperatures. Figure 2-3 shows the high-temperature hardness of tool steel, high-speed steel, cast alloy, stellite alloy (Co-Cr-W), and WC+Co cemented carbide.









