Nanoceramic bonded phase WC-based carbide refers to a type of carbide product that does not contain or contains a small amount of metal bonding agent (<0.5% by mass fraction). It has unparalleled excellent wear resistance, corrosion resistance, excellent polishing, and oxidation resistance compared to traditional carbide.
nanoceramic bonded phase WC-based carbide is a combination of ceramic hardness and carbide toughness, and products have been launched abroad. With its excellent wear and corrosion resistance, it can be used to make sandblasting nozzles, electronic packaging materials, heavy-duty sliding seal wear-resistant parts, etc.. with its excellent cutting performance, it can be used as tool and drill materials, especially for processing titanium/titanium alloys, which greatly improves work efficiency. and with its oxidation resistance and excellent polishing, it can be used as mold and decorative materials.
Characteristics of nanoceramic bonded carbide:
1Phase structure and carbon content of nanoceramic bonded phase carbide carbide are very sensitive to carbon content. For traditional carbide containing bonding phases, there is a certain range of carbon content to maintain a normal phase structure. If this range is exceeded, brittle n-phase or free carbon will appear. In contrast, the suitable carbon content of nanoceramic bonded phase WC-based carbide is not fluctuating like WC-Co alloy but is a fixed value.
2Composition design and properties of nanoceramic bonded carbide
Nanoceramic bonded carbide, which combine mechanical and wear resistance properties perfectly, are one of the most widely used ceramic-based materials in engineering. However, in most ceramic-based materials, the existence of metal bonding phases not only makes these composite materials have excellent flexural toughness but also affects certain properties, which limits their use. In addition, the low melting point of metal Co also greatly limits the application of WC-Co cutting tools in high-speed machining, which is prone to serious adhesive wear and oxidation wear. Moreover, the poor corrosion resistance, high cost, and toxicity of Co also limit the mechanical industry application of WC-Co carbide. Therefore, partially or completely replacing the Co bonding phase can expand the application of carbide. In recent years, ceramic bonding phases have attracted widespread attention in the scientific community as a new type of Co substitute.
The specific study using Nanoceramics as Binder Phase in Hardmetal Alloys
The Research Institute of Shandong University in China selected nanoscale Al2O3, ZrO2, and MgO as the binder phase for WC hardmetal alloys. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the hardmetal alloys were compared, and the toughening mechanism of the nanoceramic oxides was explored. The related paper, titled “Nano-ceramic replacing cobalt in cemented carbide as binder phase: Is it feasible?”, was published in the Journal of Alloys and Compounds.
Paper link:
https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0925838821043784

4Mechanism of Ceramic Binders Improving Toughness of carbide?Materials
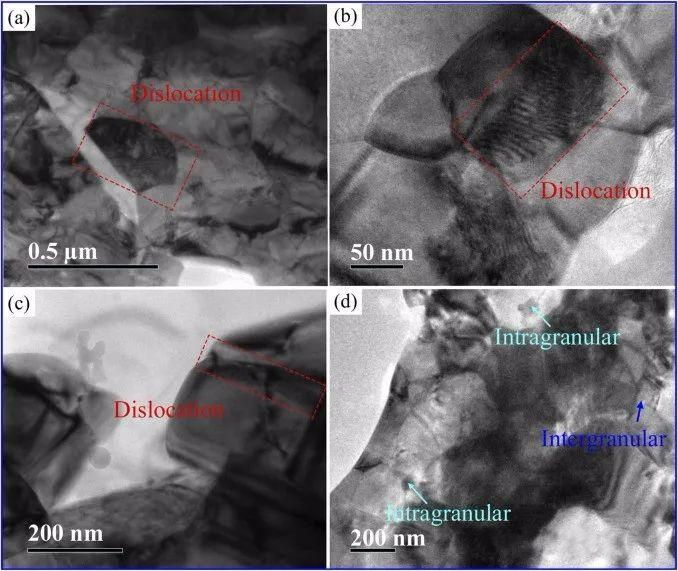
fig.1 TEM micrographs of nanoceramic bonded carbide: (a) dislocations in WC-6Al2O3, (b) dislocations in WC-6ZrO2, (c) dislocations in WC-6MgO, and (d) intragranular and intergranular microstructures of WC-6ZrO2.
After sintering, the WC grains retained their initial grain size, and the second phase significantly suppressed the grain growth of the WC matrix by limiting grain boundary migration. Dislocations were observed in all three nanoceramic bonded carbide materials, which enhanced the tolerance of the carbide. Additionally, it was found that some nanoscale ZrO2 grains were distributed along the WC grain boundaries, while more ZrO2 nanograins were distributed within the WC grains, forming so-called intragranular nanostructures. Compared with the ceramic binder phase at the WC grain boundaries, the ceramics inside the WC grains were smaller in size.
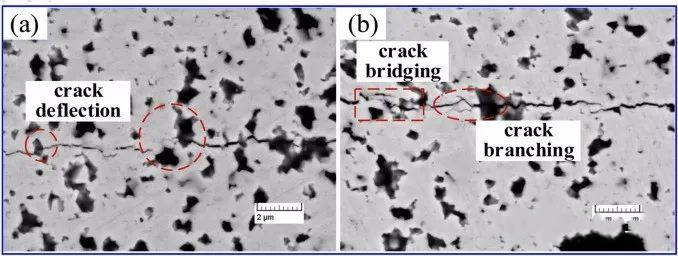
fig.2 The toughening mechanism of WC-6Al2O3
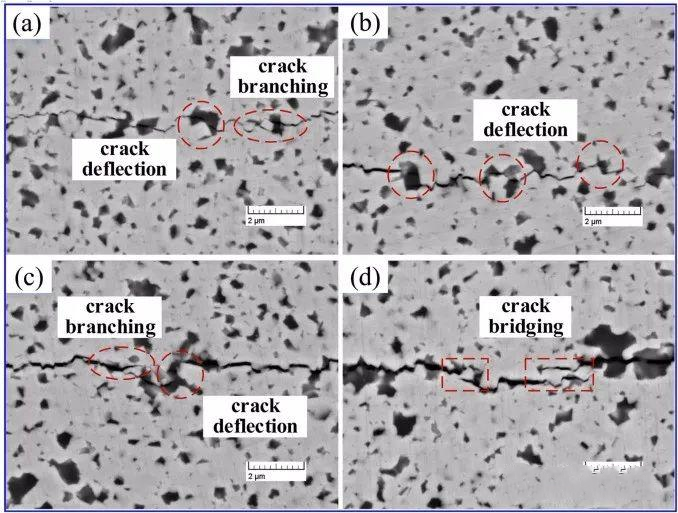
fig.3 The toughening mechanism of WC-6ZrO2
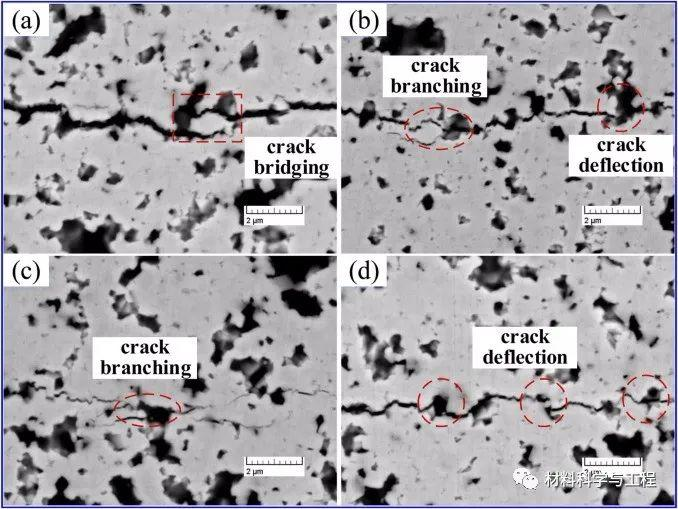
fig.4 The toughening mechanism of WC-6AMgO
During the high-temperature sintering and cooling process, residual tensile stresses are generated around the ceramic binder phase due to differences in thermal expansion coefficient, which is favorable for crack deflection when the crack reaches the stress field. When an external load is applied to the nano-ceramic binder material, the difference in elastic modulus causes a redistribution of microscopic stress, thereby increasing the material’s toughness. All three nanoceramic bonded carbide materials exhibit crack bridging, effectively reducing crack propagation energy. Non-branching cracks were also found in the carbide, greatly increasing the energy consumption of the main crack propagation and effectively slowing down crack propagation.
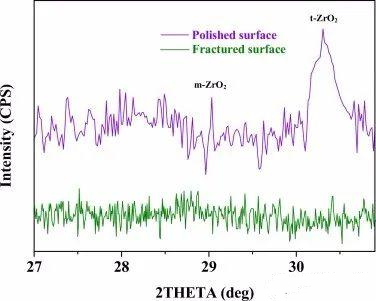
fig.5 XRD spectra of the polished surface and fractured surface of the WC-6ZrO2 specimen
During the fracture process of WC-ZrO2 carbide, when external stress is applied to the carbide, stress concentration occurs near the crack tip, promoting the transformation of t-ZrO2 to monoclinic m-ZrO2. This transformation significantly impedes the crack propagation by enhancing stress relaxation near the crack tip. In addition, the volume expansion caused by phase transformation compresses the surrounding matrix, which is conducive to crack closure. Furthermore, surface phase transformation can generate compressive stress, greatly increasing the toughness of the material.
Conclus?o
In summary, compared with traditional WC-Co carbide, nanoceramic bonded carbide exhibit a better combination of fracture toughness and hardness. Compared with micro-ceramic bonded? carbide, the hardness and fracture toughness of nano-ceramic bonded phase carbide are simultaneously enhanced. This excellent hardness of nano-ceramic bonded phase carbide is crucial for high-speed machining applications and is expected to become a candidate material for high-speed machining tools.
Deixe uma resposta
O seu endere?o de e-mail n?o será publicado.









