Experiment
Test Materials
Three types of WC-6Co cemented carbide with different grain sizes were selected for the test. The size of the cemented carbide disc was φ55mm×4mm, and the surface was rough ground, finely ground, and polished. The mating material used was Al?O? balls with a diameter of 9.5mm. Both samples were ultrasonically cleaned in acetone for 20 minutes and dried for use. The material properties are shown in Table 1.

Friction and Wear Test
The test was conducted on a UMT-2 multi-functional friction and wear testing machine produced by CETR Corporation in the United States, using a ball-on-disc contact method. The structure of the testing machine is shown in Figure 1. The cemented carbide friction disc was attached to the working table with double-sided tape, and the Al?O? ball was placed in the fixture. The two types of mating materials produced mutual movement and force of action. The friction force generated was detected by the sensor, and the curves of friction force, normal force, and friction coefficient were automatically generated by the related software according to Coulomb’s law.
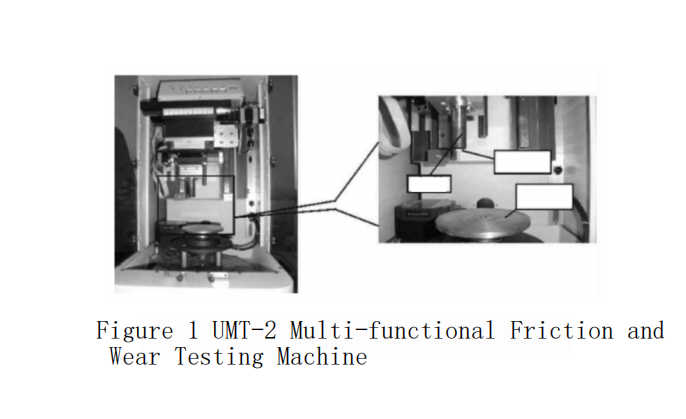
The test was conducted at room temperature, with normal forces of 10N and 20N respectively, and the linear velocities of the friction pair sliding were 40m/min, 80m/min, 120m/min, and 160m/min. The sliding distance was 500m. After the test, a scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to observe the wear scar surface morphology of the upper and lower samples, and an X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) was used to detect the elemental composition of the worn surfaces. All samples were analyzed for the elemental composition of the friction and wear surfaces under the same conditions.
Results and Analysis
Friction and Wear Performance
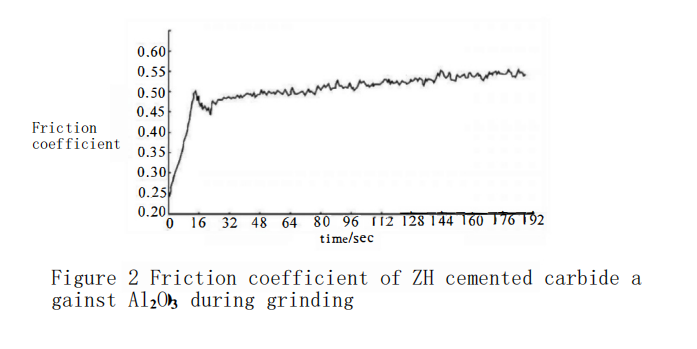
Figure 2 shows the friction coefficient curve of ZH cemented carbide drawn by the testing machine’s accompanying software (load 20N, sliding speed 160m/min). The experiment found that each friction process follows a similar pattern, that is, the initial dynamic friction coefficient undergoes a rapid increase from the initial value during the transition period, and then remains relatively stable, showing a fluctuating characteristic in the stable phase. In the beginning, under the action of the normal load, only local micro-convex bodies on the friction surface are in contact, the adhesive area is small, and the molecular attraction on the contact surface is weak, so the friction coefficient is small; as the friction process progresses, the micro-convex bodies interfere with each other, gradually get worn down, the adhesive area increases, and the molecular attraction also increases, leading to a gradual increase in the friction coefficient. The entire friction process is a continuous process of the contact surface adhering and then being sheared under the action of shear stress. Due to the peeling and breaking of the Co phase on the surface, the wear of the sample surface occurs, and the local adhesion on the surface quickly reaches a dynamic equilibrium, resulting in the friction coefficient of the surface being maintained within a relatively stable range, which is called the stable period.
Most scholars use the average value of the friction coefficient over a period of time (distance) as a characterization parameter of friction behavior. Therefore, this experiment selects the average value during the stable friction phase as the friction coefficient of the cemented carbide under the corresponding parameters. Figure 3 shows the friction coefficients of three types of cemented carbide under different loads and speeds.
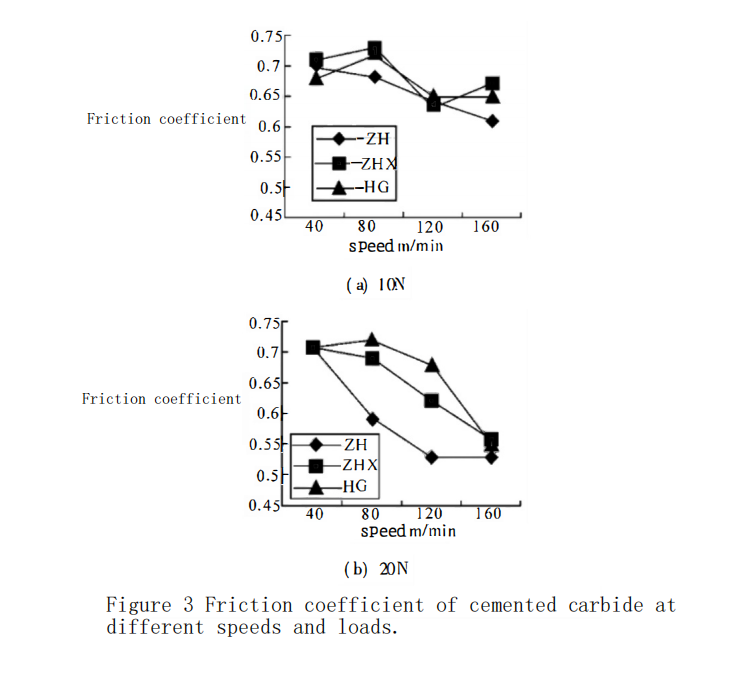
It can be seen that with the increase of friction speed and load, the friction coefficient of the cemented carbide generally shows a decreasing trend, and the decrease is most obvious in the transition from relatively low speed (40m/min and 80m/min) to high speed (120m/min and 160m/min). From the perspective of material, the friction coefficient of ZH cemented carbide is smaller than that of the other two materials, and the friction coefficients of ZHX and HG cemented carbides are not significantly different, with the friction coefficient of HG cemented carbide being slightly larger.
Wear Mechanism
After the friction and wear tests, the microstructure of the worn surfaces of each sample was observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and SEM images were taken, along with an analysis of the surface composition. The friction and wear mechanisms of the cemented carbide under different friction parameters are similar, as shown in Figure 4 (sliding speed 160m/min, load 20N).
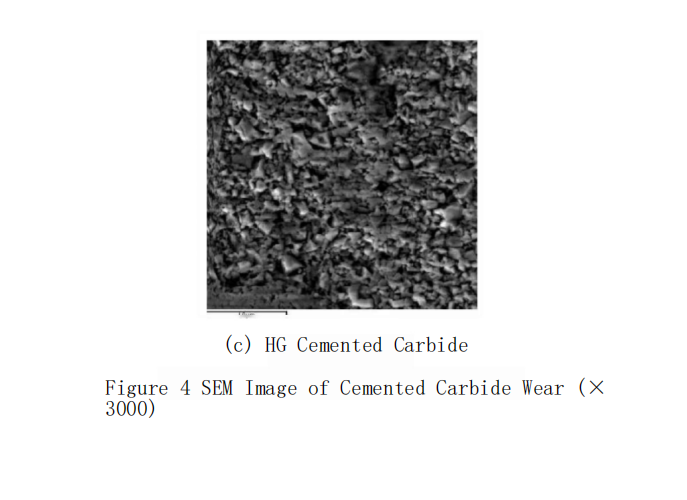
In the initial stage of cemented carbide wear, the binder phase Co undergoes plastic deformation, and the surface layer of Co is extruded by the WC grains. Due to the low hardness and good ductility of Co, under certain conditions, a micron-scale friction film can form on the surface, while the harder WC particles gradually protrude from the friction surface, preventing further rapid wear of the surface and allowing the friction process to enter a relatively stable stage. As the binder phase Co continues to be lost, the WC framework of the material is damaged, and the dislocation density within the WC particles significantly increases. When the dislocation density accumulates to a certain extent, microcracks will form on the WC particles, causing the WC particles to begin to pull out from the cemented carbide matrix. The detached WC particles remain in the wear area, transforming into abrasive particles, which, under the action of the load, compress against the matrix, resulting in new plastic deformation and grain damage.

As can be seen from Figure 4, as the grain size of the cemented carbide decreases, the grain density increases, and the degree of surface wear decreases. The surface of the ZHX cemented carbide shows no obvious shedding of WC particles, while the surface density of HG is very good, with almost no obvious shedding of WC particles. Therefore, for the traditional grain size cemented carbide ZH, the main wear mechanism is abrasive wear caused by the extrusion of the binder phase Co and the shedding of WC grains. As the grain size decreases and the density of the fine-grained cemented carbide increases, the phenomenon of WC grain spalling decreases, Co still wraps around the WC, the microstructure of the material remains intact, and most grains only undergo a certain degree of plastic deformation.
??
The size of WC grains has an important effect on the friction and wear properties of cemented carbide. As the grain size decreases, the friction coefficient slightly increases, and the wear resistance is enhanced.
The friction coefficient of cemented carbide is influenced by speed and load, and it shows a decreasing trend with the increase of speed and load.
The wear mechanism of traditional grain size cemented carbide is mainly characterized by the extrusion of the binder phase Co and the fracture and spalling of the hard phase WC grains; the grain spalling phenomenon of fine-grained cemented carbide is not obvious, and the main wear mechanism is plastic deformation.