Last week we talked about HIP. This week our topic is cold isostatic pressing, one of the processing methods of P / M materials.
It makes use of the principle proposed by French scientist Bryce Pascal that “the pressure change of the closed incompressible fluid is transmitted to every part of the fluid and its container surface continuously”. The powder material is sealed in a molding die with low deformation resistance, and liquid pressure is applied like a rubber bag. Then, by transferring the liquid pressure, the die body is uniformly compressed on its entire surface.
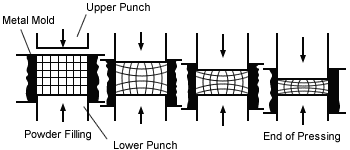
Metal molding is very similar to CIP. In this pressing method, as shown in the figure below, the powder material is filled into a space surrounded by a metal mold and a down punch. Then, they are compressed by reducing the distance between the upper and lower punches.
Industrial metal molding equipment has a series of automatic processes from powder filling to mold removal. The single action press shown in the figure below compresses the powder into a shape with the lower punch fixed. Due to the friction between the powder and the metal die or punch, as well as between the powder particles, the lower part of the molding body will have a lower density than the upper part.
The difference between CIP and metal molding
In principle, they have different pressurization processes. CIP applies isostatic pressure to materials using liquid pressure, while metal molding is only applicable to uniaxial pressure. As a result, CIP can produce density and even products because there is no friction with the metal mold. The right figure compares the density distribution of CIP and metal molding products.
CIP processing type
According to the relationship between powder filled mold and pressure medium, CIP forming methods are divided into wet bag method and dry bag method.
Wet bag method
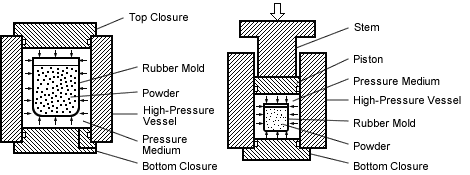
In the wet bag process, as shown in the figure below, the powder is filled in the forming mould and sealed outside the high-pressure vessel before being directly immersed in the pressure medium. Then, isostatic pressure is applied on the surface of the die to compress the powder. This method is suitable for small batch production and trial production of various complex shapes or large products.
There are two types of structure: the external pressurized type shown in the left figure, which pressurizes the pressure medium into the pressure vessel from the outside; the piston direct pressurized type shown in the right figure, which pressurizes the pressure medium sealed in the pressure vessel directly, and installs the piston instead of the top cover.
Dry bag method
The dry bag method is to transfer the pressure through the pressed rubber mold in the high-pressure vessel and fill the powder in the formed rubber mold, as shown in the figure below. The method is labor-saving and highly automatic, and is suitable for the production of simple and limited products.
The dry bag process is divided into two systems: the circumferential + axial compression system (left) and the circumferential compression system (right), as shown in the figure below.
The circumferential + axial pressure system applies pressure from the outer surface of the mold and the top surface of the cover type rubber pressing die, as shown in the figure below.
The circumferential pressurization system only applies pressure from the outer surface of the molded rubber mold through the cylindrical rubber pressing mold, as shown in the figure below. However, due to the fluid properties of the powder, the pressure applied to the green compacts is almost equal to isostatic pressure.