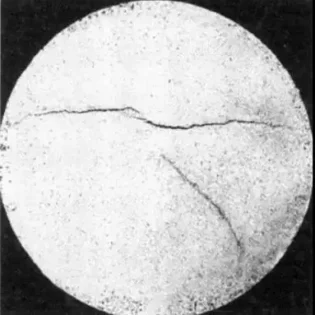
Non metallic inclusions mainly come from various types of non-metallic inclusion compounds formed by the corresponding increase of the equilibrium constants of oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen compounds in the process of liquid steel condensation. The products formed by chemical reaction should be called non-metallic inclusion or inclusion for short. Although the amount of inclusions in steel is small, it has a bad effect on the quality of steel materials and products. With the development of modern material engineering technology, the requirement of steel quality is increasingly strict. Therefore, in-depth study of non-metallic inclusions will be of great significance to material identification, product fracture analysis, scrap analysis and failure analysis.
1.Sources of non-metallic inclusions in steel
Inclusions are mainly caused by a series of physical and chemical reactions during melting and solidification of steel. According to their sources, they can be divided into endogenous (internal) inclusions and exogenous (external) inclusions.
endogenous inclusions
Endogenetic inclusions refer to the products produced by the chemical reaction between various material components in the process of steel smelting, casting and condensation, or the contact between the steel and the atmosphere or container in the furnace, or the particles precipitated due to the decrease of solubility when the condensation temperature of liquid steel decreases.
foreign inclusions
Foreign inclusion is also called external inclusion or accidental inclusion. It is due to the smelting, casting production process, from the equipment or container off and mixed into the liquid steel impurities. In addition, sometimes due to the negligence of smelting operation, the refractory brick cracks and falls off due to thermal impact, forming products with other kinds of oxides and becoming foreign inclusion
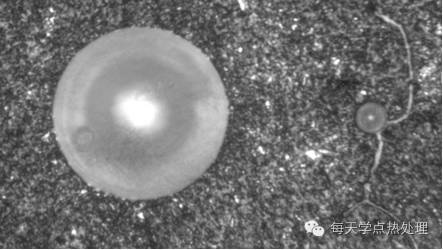
2.Influence of inclusions on steel quality
The harmfulness of inclusions depends on their quantity, shape, size, distribution, melting point, physical and chemical properties. When the inclusion has the property of low melting point, the steel will produce hot brittleness and crack due to its melting or softening during hot working. When there are aluminum inclusions or other nitrides in the steel, the surface hardness of the steel is not uniform, which makes it difficult to cut and grind. When the inclusion in the steel has exceeded the standard, it will bring great difficulties to the heat treatment and welding process, such as the uneven infiltration layer in the chemical heat treatment, and the strength of the weldment will be greatly reduced or cracked during welding
3.Metallographic identification of inclusions
Metallographic identification method can not identify the chemical composition and crystal structure of inclusions, but can directly observe and identify the shape, size, quantity, distribution and type of inclusions under optical metallographic microscope. At the same time, metallographic identification method also has the characteristics of simple operation and easy implementation.
interception and preparation of metallographic samples in order to ensure that the intercepted samples can represent the results of identification of non-metallic inclusions, the intercepted parts shall meet the requirements of corresponding technical conditions. For forging blank, samples can be taken from different parts from the center to the edge of forging blank, such as the head, middle and tail of forging blank; for rolled and cold drawn steel, samples should be taken longitudinally through the center line; for quenching crack, forging crack, hot rolling, stamping and failure fatigue fracture, samples should be taken at the crack and fracture; for special steel or product parts, samples can be taken according to the requirements It should be carried out according to the standard of the company.
The metallographic sandpaper from coarse to fine shall be used in the grinding process of the sample. The next grinding process shall be perpendicular to the grinding mark of the previous grinding process until the grinding mark disappears. In the polishing process, the polishing surface of the sample should be moved back and forth at the radius of the polishing disc with appropriate pressure, and the sample itself should also be rotated continuously. The final requirement is that the sample is not etched in 100 times field of view, and its surface has no scratch, no peeling, no water mark, no stain, smooth and bright as a mirror.
4. types and morphology of inclusions
Sulfides have high ductility, single gray inclusions with a wide range of shape ratio (length / width), generally with rounded ends; most of alumina have no deformation, with small shape ratio (generally < 3), and black or blue particles are arranged in a row along the rolling direction (at least three particles); silicate has high ductility, with a wide range of shape ratio Single black or dark gray inclusions (generally ≥ 3), generally with acute angle at the end; spherical oxides are non deformable, angular or round, small in shape (generally < 3), black or blue, irregularly distributed particles; single particle spherical inclusions are round or nearly round, diameter ≥ 13 μ M.