Le inclusioni nell'acciaio fuso durante la fusione sono uno dei motivi importanti per le crepe nelle fusioni di acciaio. Al fine di ridurre le inclusioni nell'acciaio fuso, le operazioni di fusione di disossidazione, desolforazione, rimozione delle impurità e degasaggio dovrebbero essere rafforzate nel processo di fusione e dovrebbero essere prese le misure necessarie nella siviera dietro il forno, come l'aggiunta di terre rare per modificare il forma delle inclusioni, in modo da ridurre l'esistenza di inclusioni ed eliminare meglio le cricche delle fusioni di acciaio.
1. Types and causes of inclusions in steel
Inclusions in steel mainly refer to non-metallic inclusions in steel. It is generally believed that non-metallic inclusions in steel usually exist in the following forms: oxides: F EO, Fe2O3, m no, Al2O3, SiO2, MgO, etc.; sulfides: m ns, FES, etc.; silicates: fesio 4, m nsio 4, FeO · a L2O3 · SiO2, etc.; nitrides: AlN, Si3N4, etc.
The non-metallic inclusions in steel come from two aspects: one is generated along with the smelting process, namely, deoxidizing products of ferroalloy are added during tapping and secondary oxidation products of molten steel and air during pouring, which are called endogenous inclusions, which are generally small particles and evenly distributed in steel; the other is brought in from outside for various reasons, which are called foreign inclusions, This kind of inclusions are mostly irregular in shape, large in size and uneven in distribution, which is the main cause of cracks and is harmful to steel.
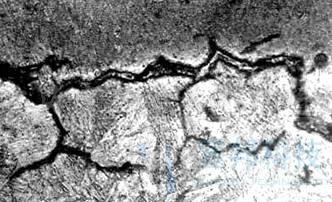
The endogenetic inclusions are mainly produced in the following situations: ① in the smelting process, the deoxidized products are not completely eliminated, or the temperature drops during the pouring process, and the deoxidized products generated by the continuous reaction are too late to float and remain in the molten steel, some of them exist in the matrix structure of the steel with small particles, some of them gather into large particles Al2O3), Some of them exist in steel in solid solution state (such as m no and f EO); ② in the process of tapping and pouring, the molten steel is oxidized in contact with air, and oxygen combines with elements in steel to form secondary oxide and remains in the molten steel; during the solidification process of molten steel, FES and FeO with low melting point are separated and crystallized from the molten steel, and finally precipitated at the grain boundary and between dendrites.
Foreign inclusions: this kind of inclusions are mainly brought in by the raw materials, such as sediment, slag and protective slag. The refractory materials of the pouring system are washed and etched by the molten steel, and remain in the molten steel, most of which are large particle inclusions.
The non-metallic inclusions are dissolved in the molten steel or exist in the molten steel alone at high temperature. However, with the decrease of temperature and the change of composition, gas pressure and other conditions, the inclusions originally dissolved in the molten steel will be separated as independent phases and gathered on the grain boundary during the crystallization process, becoming the micro unit for cutting the connection of cast steel matrix and the initial source of cracks, Thus, the potential hidden danger of crack is formed.
2. Relationship between main inclusions and cracks in cast steel and measures to reduce them
In the non-metallic inclusions, the main reason for the cracks of steel castings is sulfide inclusions, which often act together with other factors to increase the crack tendency of steel castings. In cast steel, sulfide inclusions are divided into three types: type I – spherical; type II – point chain like intergranular film; type III – arbitrarily distributed sharp angle. Among them, class II inclusions are the most harmful to steel, class III is the second, and class I is the least. The sulfide inclusions are related to the degree of deoxidization and the amount of residual aluminum in steel. When the amount of aluminum solid solution is low and the amount of oxygen remains little, class I inclusions can be obtained.
Deoxidizer has great influence on the formation of inclusions and the properties of steel. The deoxidizing effect of the composite Deoxidizer is better than that of the single deoxidizer, because the inclusions formed by the composite Deoxidizer are large and easy to float up and remove. If the deoxidation of molten steel is not enough, it is easy to have porosity and crack. However, the amount of aluminum used for final deoxidation is just enough to deoxidize without remaining, the amount of aluminum solid solution is low, and the amount of oxygen remaining is small, which will result in class II inclusions. Generally, excessive aluminum deoxidization will result in class III inclusions. It should be noted that if excessive aluminum is used, more aluminum nitride inclusions will precipitate along the grain boundary, resulting in “rock like” brittle fracture and deterioration of steel properties. Therefore, it is unreasonable to deoxidize with excessive aluminum. The amount of aluminum added and the residual aluminum in steel should not be too low or too high.
Aluminum deoxidization is a widely used method of steel deoxidization. Two deoxidizing processes are usually used in industrial production, one is adding aluminum deoxidizing process, the other is controlling aluminum deoxidizing process. The former is to completely remove the dissolved oxygen in the steel with aluminum, and then remove the Al2O3 inclusion as much as possible through various ways of agitation; the latter is to roughly deoxidize only with silicon manganese, and strictly control the aluminum and calcium content in the steel, so as to control the composition, property and morphology of the oxide inclusion precipitated in the steel [3]. The first deoxidation rate of the former is more than 90, and the deoxidation product is mainly Al 2O 3; the second one is greatly reduced, and the first deoxidation product is mainly SiO2.
Foreign inclusions can be removed according to their sources, while endogenous inclusions need to be controlled by deoxidation and calcium treatment.
In ladle refining, more and smaller argon bubbles are blown into the molten steel to remove the primary deoxidation products.
In order to better remove inclusions and reduce cracks in steel, the following measures are taken for smelting operation.
(1) Prepare raw materials to prevent foreign inclusions.
(2) Adopt reasonable steelmaking process: such as adopt reasonable oxygen blowing and power distribution process, ensure a certain decarburization speed to make inclusions float up, and maintain good furnace condition. (3) Compound Deoxidizer is used instead of single deoxidizer. (4) Adding rare earth in the ladle after the furnace can change the shape of inclusions, reduce inclusions and reduce the cracking of steel castings










