What is cemented carbide?
Carbide is a composite material, usually made by sintering with methods such as powder metallurgy, including refractory metal carbides (carbides of titanium, molybdenum, tungsten, tantalum, niobium, etc.) and binding metals (nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, cobalt, etc.). Carbide has excellent mechanical properties, good wear resistance, oxidation resistance, and thermal stability. It is widely used in metal cutting and forming applications, abrasive slurry nozzles, mechanical seal rings and bearings, oil drilling, etc., and is known as the “teeth of industry.”
Traditional manufacturing methods of cemented carbide
Carbide is generally prepared by traditional methods such as injection molding, extrusion molding, die pressing, hot pressing, hot isostatic pressing, spark plasma sintering, etc. In addition, surface modification methods such as plasma spraying, reaction flame spraying, tungsten inert gas (TIG) arc melting, and laser surface treatment have been applied to the preparation of carbide coatings and clad materials.
The disadvantages of traditional hard alloy forming methods
Currently, the preparation technology of carbide still faces some serious technical challenges, including:
Carbide product preparation is entirely dependent on molds, which have high costs, long cycles, and high subsequent processing costs (often accounting for more than 50% of the cost), which greatly affects the manufacturing cost of cemented carbide.
Many complex-shaped carbide products cannot be prepared by conventional and advanced powder metallurgy methods, such as hollow parts, internal holes, internal grooves, small angle bends, and chip breakers of cutting tools, which severely limit the structural design space of carbide products.
Traditional carbide preparation technology cannot achieve the preparation of multifunctional/variable functional composite structure and gradient structure cemented carbide, which obviously hinders the expansion of the application field and the play of advantages of carbide.

The additive manufacturing method of? carbide: laser sintering
Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a disruptive technology that can accumulate materials layer by layer based on designed CAD files to form complex-shaped parts. AM technology can easily achieve the production of complex-shaped parts and is expected to reduce the production cost of carbide. Therefore, additive manufacturing of carbide is increasingly being valued.
The main technical means include powder bed fusion (PBF), such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing (EBM), and Directed Energy Deposition (DED), such as Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS) and Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM).
Due to the high melting point of carbide, the use of additive manufacturing technology still poses great challenges. Currently, the additive manufacturing technologies that have been used for carbide mainly include: Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS), Binder Jetting 3D Printing (3DP), and 3D Gel Printing (3DGP).
Advantages of 3D laser printing in AM
Additive manufacturing technology can successfully produce cemented carbide parts with good mechanical properties and near theoretical density, but there are also many problems. Cracks, pores, and surface roughness are inevitable quality defects in additive manufacturing of cemented carbide, and the unique microstructure formed by the repeated heating and cooling process of additive manufacturing also affects the part’s performance. Post-processing methods such as hot isostatic pressing and heat treatment will bring additional time and cost, hindering the development of additive manufacturing of cemented carbide.
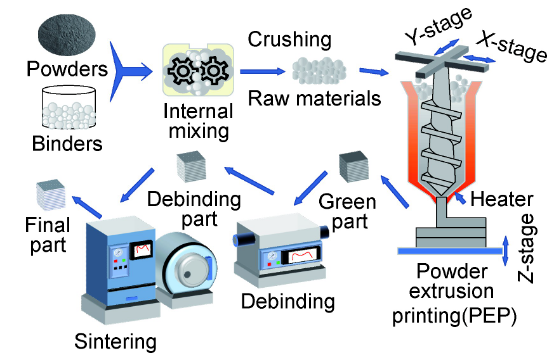
Main species of 3D laser printing for cemented carbide
SLS technology and LENS forming technology
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is one of the rapid prototyping (RP) technologies, which include indirect laser sintering (EMLS) and direct laser sintering (DMLS). It can directly manufacture three-dimensional (3D) parts of any shape using metal powder and is suitable for small batch manufacturing of cemented carbides. SLS forming technology for cemented carbides often requires subsequent processing, such as element infiltration to improve comprehensive performance. Adding rare earth oxides as nucleation sites can refine the grain size and improve the relative density and microhardness of the parts.
While Increasing the laser power density and powder feed rate in LENS forming technology of hard alloy can result in higher sample height and improved forming quality. Alloys prepared by LENS have inconsistent mechanical properties in the height direction and exhibit a layered structure similar to SLM, with the build direction affecting the microstructure.
3D Laser Printing Forming Technology
The 3DP forming technology of cemented carbide operates at a lower temperature, avoiding element evaporation and resulting in a uniform microstructure and improved wear resistance. By using a binder metal such as nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, or cobalt, and subsequent infiltration, parts comparable to traditional cemented carbide can be obtained. The 3DGP forming technology of cemented carbide generally does not have obvious cracks or void defects, and has a uniformly distributed microstructure and excellent mechanical properties.

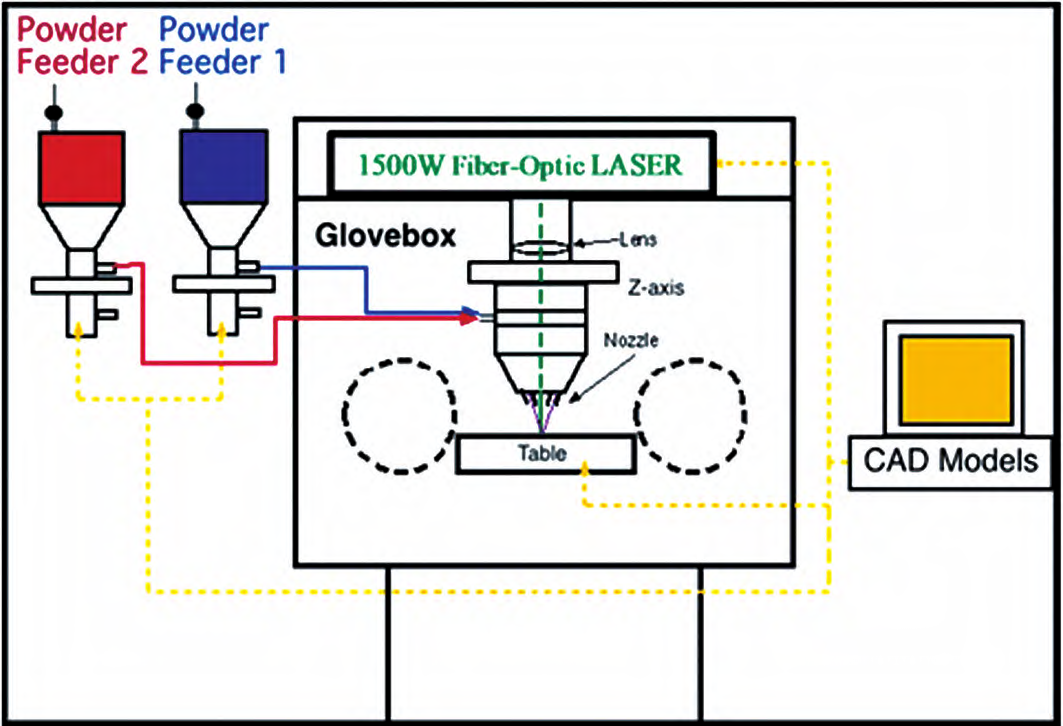
selective laser melting (SLM) technology
selective laser melting?technology uses high-energy lasers to completely melt metal powder, which then solidifies quickly through rapid cooling to form the desired shape. Compared to SLM printing of metal materials, SLM printing of cemented carbides is much more difficult and the densification mechanism is more complex. The main reason for this is that during the SLM printing process, only the Co binder phase can melt, while the WC ceramic phase has a very high melting point (greater than 2700℃) and will not melt during the printing process, which seriously hinders the densification process of cemented carbides.
The selective laser printing technology of cemented carbide is prone to cracks and voids defects, which can be avoided by appropriately increasing the Co content in the WC-Co alloy to prevent the generation of brittle phases and reduce crack sensitivity. The microstructure of the alloy can be controlled through the process. Based on these characteristics, different microstructure can be obtained by adjusting the energy density. For carbide, high energy density produces a brittle microstructure with small WC grains and low Co content, while low energy density produces a tough microstructure with large WC grains and high Co content. Controlling the microstructure through the process is an important means of SLM preparation of parts, but further research is still lacking.
The Future of Additive Manufacturing for carbides
Currently, selective laser printing has difficulty producing cemented carbide parts with nearly theoretical density, and further research is needed to study the relationship between process, part quality, and microstructure. Compared to SLM, 3DP and 3DGP can produce parts with better performance and more uniform microstructure, but with lower dimensional accuracy and more complex processes, process improvement or corresponding post-processing should be considered. One of the main applications of additive manufacturing of cemented carbides is the production of cutting tools and molds. Therefore, the cutting durability, fracture behavior, and wear mechanism of corresponding parts should be further studied. To expand the applicability of additive manufacturing of cemented carbide parts, future research should combine traditional processes such as hot isostatic pressing to further improve the overall performance of the parts and meet the requirements of complex part manufacturing.









