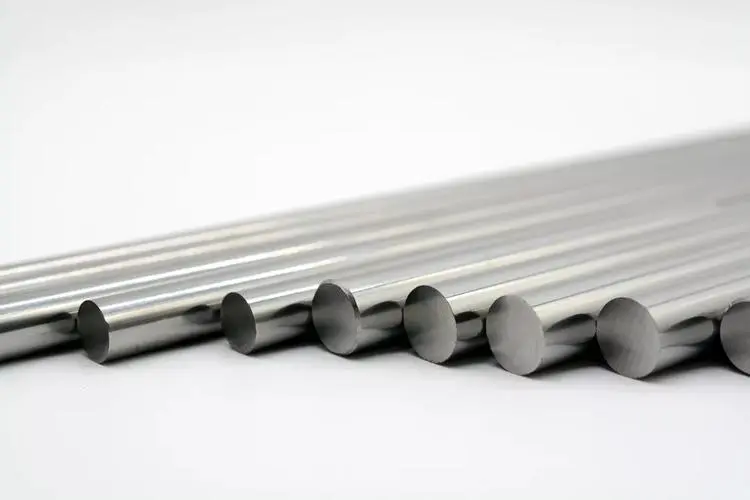
Powder Extrusion Molding (PEM)
Powder extrusion molding (PEM) involves the extrusion of a mixture of powder, binders, plasticizers, etc., through a die nozzle to obtain the desired shape and size of the blank. The basic process of PEM includes powder mixing, granulation, extrusion molding, debinding, and sintering. PEM can be operated at low temperature and low pressure, with no limitation on the length of the product, uniform longitudinal density, and advantages such as strong forming continuity, low cost, and high efficiency, making it the main method of forming carbide?round bars today. Additionally, the use of hot extrusion molding has been adopted to prepare dispersion-strengthened materials and high-temperature alloys.
Powder Injection Molding (PIM)
Powder injection molding (PIM) combines traditional plastic molding processes with powder metallurgy technology. It involves mixing powder and molding agents, granulating, heating in an injection molding machine to form a flowable material, injecting into the mold cavity under pressure, and obtaining preformed blanks with uniform structure and complex geometry. Products produced by this method have good surface finish and shapes close to the final product. PIM improves the sintering performance by maintaining good flowability of the carbide rod powder during injection and enhancing the interaction between binders and alloy powders. Compared to traditional molding methods like die pressing, PIM offers advantages such as unrestricted product shapes, uniform product density, wide applicability, and consistent shrinkage of product parts, allowing better control of dimensional tolerances.

Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)
Cold isostatic pressing (CIP) involves placing carbide rod powder in a closed liquid environment at room temperature to form the powder under ultra-high pressure transmitted by the liquid. The pressure transmitted by the liquid medium during isostatic pressing is equal in all directions, resulting in uniform stress on the blank and significantly improved product performance. Typically, preforms are obtained through metal die pressing followed by cold isostatic pressing. After sintering, carbides produced by cold isostatic pressing exhibit low shrinkage, high density, and hardness.
Explosive Forming (EF)
Explosive forming is a special method of compacting blanks using intense explosive pressure. It involves placing explosive substances around a shell containing superhard powder. The enormous pressure generated during the explosion (up to 10 MPa) can rapidly compact blanks with very high relative density. Experiments have shown that the density of WC-8Co composite powder can reach 99.2% using explosive forming.
High Velocity Compaction (HVC)
High velocity compaction (HVC) involves compacting powder at pressures of 600 to 1000 MPa and velocities of 2 to 30 m/s using hydraulic-controlled heavy hammers. Compared to traditional die pressing, HVC achieves significantly faster compaction rates, up to 500 to 1000 times faster. This technology improves material properties, and the repeated compaction characteristic enables small to medium-sized equipment to produce large-sized components.

Warm Compaction (PM)
Warm compaction involves pressing carbide rod powder at temperatures of 100 to 150°C in heated molds to obtain blanks. The process effectively increases the density and strength of the pressed blanks. Recently, flow-assisted warm compaction (WFC) has been developed based on warm compaction, which has the capability to manufacture high-density parts with complex geometries, offering broad prospects for the manufacturing of parts with complex shapes such as side cavities and threaded holes.
Extrusion molding of carbide double helix hole bars
The so-called inner helical hole bar refers to the part of the spiral cutting tool that forms spiral cooling holes. When the tool is in operation, the inner holes can pass coolant, reducing the processing temperature. The angles of the cooling holes and the cutting edge of the drill tool are synchronized, typically at 45°, 30°, and 15°; the most commonly used conventional tool spiral cooling hole angle is 30°.
External helix extrusion for helix hole carbide rod
External helix extrusion involves the use of grooves on the male mold to forcefully change the direction of the extruded fluid material, rotating it to extrude the billet. The manufacturing of the cooling hole core rod is synchronized with the rotation direction of the mold thread. The entire process requires complex mold design and is similar to ordinary extrusion methods, making it one of the most widely used extrusion techniques domestically and internationally.
Internal helix extrusion
Internal helix extrusion utilizes the special structure of a double helix extruder to extend the core rod to the extrusion screw, rotating the core rod by the screw to achieve the helical action. This process has simpler mold design but requires strict control over extrusion parameters: the extrusion speed of the fluid and the rotation speed of the core rod must maintain a fixed proportion; otherwise, the geometric parameters of the product may not meet requirements. The fluid motion during extrusion is similar to that of other rods.
Due to the difficulty of this technique,there are a handful of companies possessing the capability of production, among which Meetyou Carbide stands out. There is not much difference in the extrusion method between triple helix holes and double helix holes, only the design of the core rod in the mold differs.