Development of Grades
Due to the combination of coating technology and the carbide matrix with high toughness and high hardness, the market segmentation of standard K and P type carbides is changing, and the application range of K type carbides is still expanding. The development process of extruded grades is as follows.



K10/20, with a cobalt content of about 6%, contains approximately 0.2% VC and 1% TaC, and the grain size of WC is between 1.0 and 1.5 μm. Since large TaC grains (>2 μm) are prone to premature shedding during cutting, and also reduce the toughness of the carbide, which is the biggest taboo for K-type carbides, the TaC in this grade carbide?has been replaced by Cr?C?. Subsequently, the K20F grade appeared, with a cobalt content of about 8%, and the WC grain size reached 0.7 μm, mainly used for PCB micro-drills and twist drills. When extended to cutters for paper processing, the cobalt content increased to 8.5%, and the WC grain size was 1.0 to 1.5 μm. Jinlu Company’s GK10, GK20, and GK20UF correspond to these grades. The typical microstructures of GK10, GK20, and GK20UF grade carbides are shown in Figures 1, 2, 3, and 4.
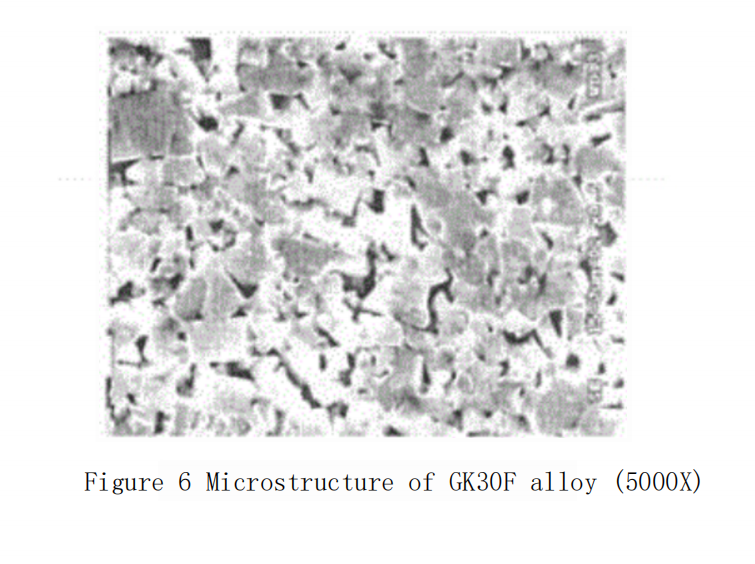


ISO grade K30-K40, with a cobalt content of 10%, also adds Cr?C? and VC. The WC grain size is between 0.6 and 0.8 μm. This grade of carbide?has high strength (TRS reaching 4000 MPa), high hardness (HRA 92.2), and high wear resistance. It is important to note that the total content and the ratio of Cr?C? and VC have a significant impact on the hardness and strength of the carbide, and for different processing objects, the content and proportion of Cr?C? and VC need to be selected. To this day, this grade is still one of the main grades for rods. Jinlu Company’s GK30F grade corresponds to this. The typical microstructure of the GK30F grade carbide?is shown in Figures 5 and 6.
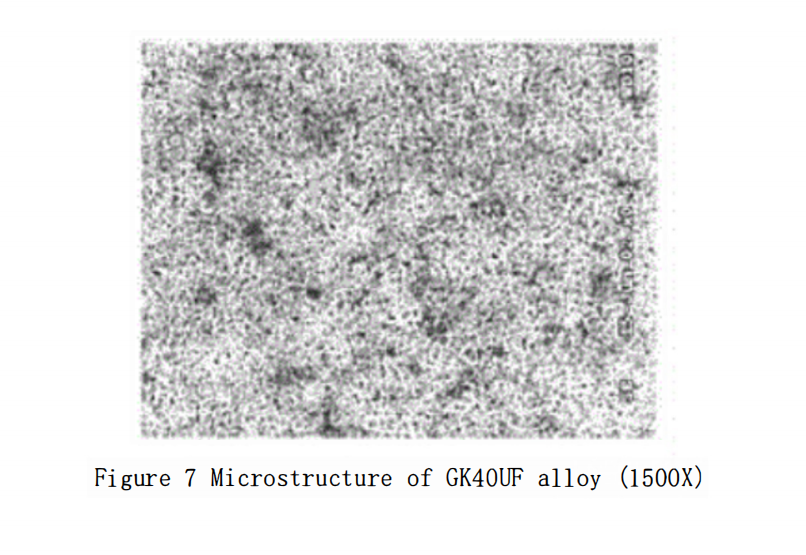

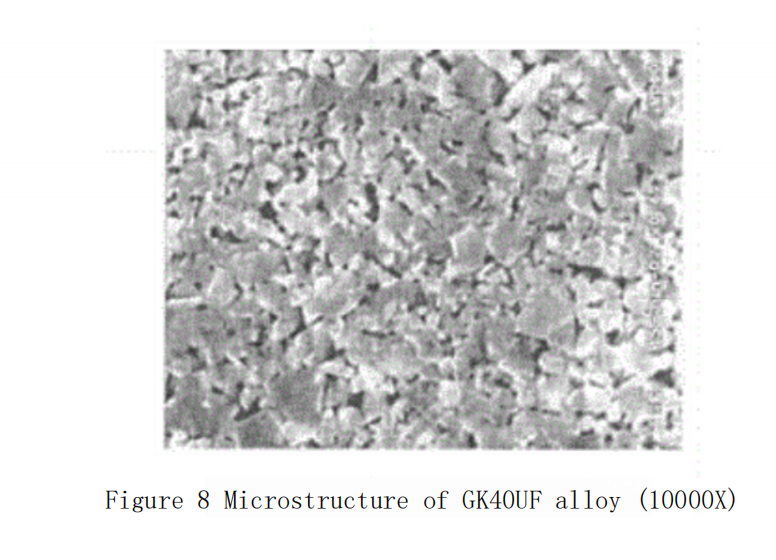
Japanese manufacturers were the first to develop hard metal drills and end mills with a cobalt content of 12%, while also adding Cr?C? and VC (totaling 1.2%), with a WC grain size of 0.4 μm. The wear resistance and toughness of this grade of carbide?are significantly improved, thereby significantly extending the tool life. It has outstanding advantages in the processing fields of hardened steel, stainless steel, titanium carbides, and glass fiber-reinforced plastics. The processing performance advantages of this grade are becoming more apparent and it is replacing the GK30F grade in many application areas. Jinlu Company’s GK40UF grade corresponds to this. The typical microstructure of the GK40UF grade carbide?is shown in Figures 7 and 8.

The ultra-fine grade currently under development, which contains a cobalt content of 12% and a WC grain size of 0.2 μm to 0.3 μm, and also contains VC and Cr?C? inhibitors, is widely favored by the industry. The microstructure of the test sample for Jinlu Company’s GK30SF grade is shown in Figure 9.
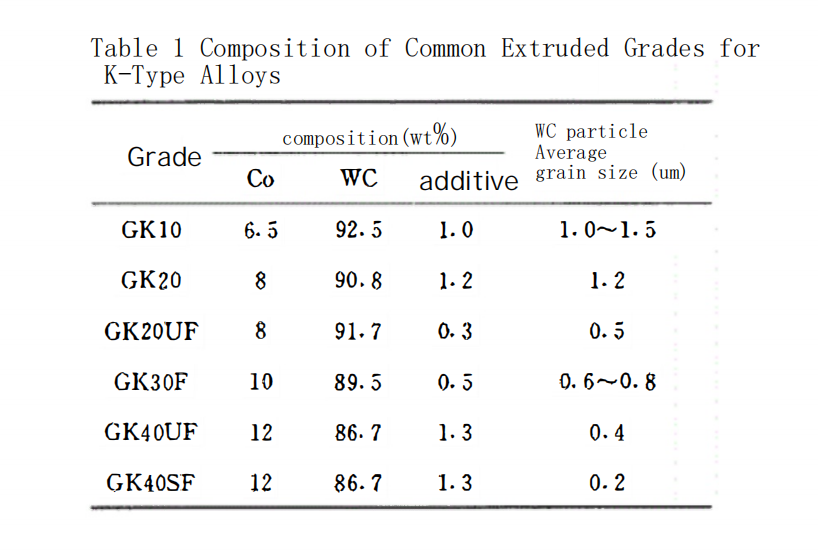
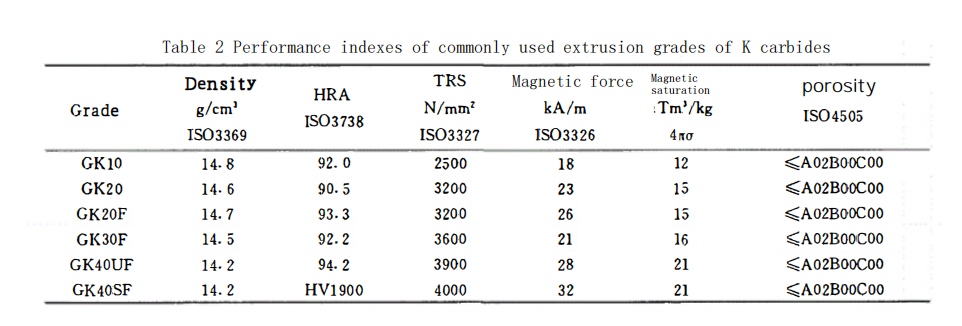
Tables 1 and 2 list the composition and performance indicators of the aforementioned grades.
Development of Production Technology
Production Method of Extrusion Materials
The production process of extrusion materials is as follows: wet grinding (both rolling ball milling and stirring ball milling can be used) → slurry drying → blending with a forming agent → screening and granulating. It must be noted that a considerable number of extruded product grades contain one or two types of trace grain growth inhibitors, therefore the selection of WC powder and cobalt powder grades and the method of adding grain growth inhibitors will fundamentally affect the performance of the carbide.
Extrusion Methods
Currently, the extrusion machines used in the production of hard metal extrusions include plunger extruders and screw extruders.
Plunger extruders’ output per working cycle is limited by the volume of the plunger cavity. Different tonnage plunger extruders have varying single loading quantities, ranging from a few kilograms to several dozen kilograms. Their advantage is flexible production scheduling, convenient switching between different grades of materials, and minimal material loss.
Screw extruders have almost unlimited production capacity, with continuous feeding and extrusion, which is highly suitable for the mass production of established grades. The downside of screw extruders is that equipment cleaning and installation are time-consuming when switching grades, and there is a significant waste of materials.
Both plunger extruders and screw extruders, advanced extrusion technology manufacturers have made progress in the automatic placement and automatic cutting of the compact. The extrusion molding of porous synchronous extrusion and double helix cooled bar stock is a reflection of the overall advancement of extrusion technology (see Figures 10 and 11).
Method of Removing Forming Agents
The composition of the extrusion forming agents and the corresponding process for removing them are topics that manufacturers have continuously researched. The motivation for this research comes from reducing costs and improving the dimensional limits of extruded molding. The traditional process involves removing the forming agent in a hydrogen atmosphere, followed by vacuum low-pressure sintering. Technologically advanced manufacturers have made breakthroughs in forming agent research, with the extrusion blank first being dried in an oven (without the need for a protective atmosphere) before undergoing vacuum low-pressure sintering. The drying process and equipment are shown in Figures 12 and 13.
Sintering Technology
Extruded profiles all use vacuum low-pressure sintering processes to ensure the uniformity of the product’s material and the stability of production.
Inspection and Performance Evaluation
In addition to the conventional analysis indicators of the carbide, the quality inspection of extruded profiles also includes ultrasonic testing for the sintered blanks of rods with a diameter of more than 12mm. Attention should be paid to the dispersion of the product’s bending strength and the fluctuation of the coercive force. For micro-drill rod materials used in PCBs, special attention must be given to controlling the carbide’s hardness, bending strength, and magnetic saturation value; all three indicators must be controlled simultaneously.

Conclusion
Just like with die-pressed cemented carbide products, there is a significant gap between China’s extruded cemented carbide profiles and the world’s advanced level. The main aspects of this gap are as follows:
- Material quality disparities
- Disparities in binder and pre-sintering technology
- Inability to produce, or produce stably in bulk, cutting-edge products
- Automation disparities
- Stability of industrial production (within the same batch or between different batches)
Therefore, we should increase our research and development efforts in the aforementioned areas to quickly narrow the gap with the world’s advanced level. This will provide reliable domestically produced cutting tools for China’s emerging electronic industry and machinery manufacturing industry.









