
The structure and working principle of a toothed wheel drill bit
A toothed wheel drill bit primarily consists of three components: the toothed wheel, bearings, and the drill bit body. The toothed wheel is the core component of the drill bit, composed of multiple teeth embedded on the wheel’s surface. These teeth continuously impact and break rock formations as the toothed wheel rotates, enabling the drilling operation.
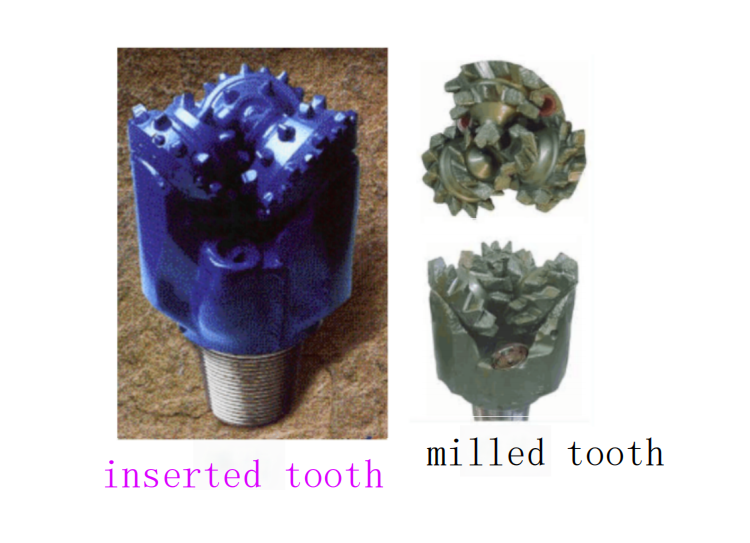

Milled-tooth wheel drill bit
The teeth of a milled-tooth drill bit are machined from the toothed wheel blank, primarily in the form of wedge-shaped teeth. Depending on their location, these teeth are categorized as gauge teeth, inner-row teeth, and chisel teeth. Chisel teeth are embedded with carbide for enhancing gauge retention. The determination of tooth structure parameters takes into account both their effectiveness in breaking rocks and the teeth’s strength.
Generally, drill bits designed for soft formations have larger tooth height, tooth width, and tooth spacing, while those for hard formations have the opposite characteristics. To enhance the wear resistance of milled teeth, a carbide wear-resistant layer is deposited on the tooth surface.
Feature of milled-tooth wheel drill bit
The teeth of milled-tooth drill bits are directly machined from metal materials, and the tooth shape, width, and height can be designed and processed according to the characteristics of the geological formation. Therefore, they exhibit high mechanical drilling speed in soft formations.
The material of milled teeth is limited by the toothed wheel material. Despite the application of carbide overlay through welding, their wear resistance is still insufficient. In hard and highly abrasive formations, their service life is significantly reduced.
Inset toothed wheel drill bit
Insert toothed wheel drill bits are created by drilling holes into the toothed wheel and then fitting teeth made of carbide materials into these holes.
?? carbide teeth used on toothed wheel drill bits are typically composed of tungsten carbide (WC) and cobalt (Co) series carbides. These alloys are fabricated through powder metallurgy methods, with tungsten carbide powder as the skeleton metal and cobalt powder as the binder. Sometimes, a small amount of tantalum or niobium carbides is added. With an increase in cobalt content in the alloy, density decreases while hardness gradually decreases, indicating reduced wear resistance. However, flexural strength increases, and impact toughness also improves. Without altering the tungsten carbide and cobalt content, increasing the grain size of tungsten carbide can enhance the toughness of the carbide, while its hardness and wear resistance remain unchanged. In recent years, diamond composite material insertshave been developed.
Inserts form the cutting structure at the bottom of the well. Depending on the position of the teeth in the cutting structure, teeth can be categorized as inner-row teeth, gauge teeth, and chisel teeth.
Shapes of tooth on insert toothed wheel drill bit
The shape of the teeth on an insert toothed wheel drill bit is designed based on the geological formation conditions. In general, pointed and long teeth are suitable for soft formations, while short and blunt teeth are better suited for hard formations. Representative tooth shapes are described as follows:
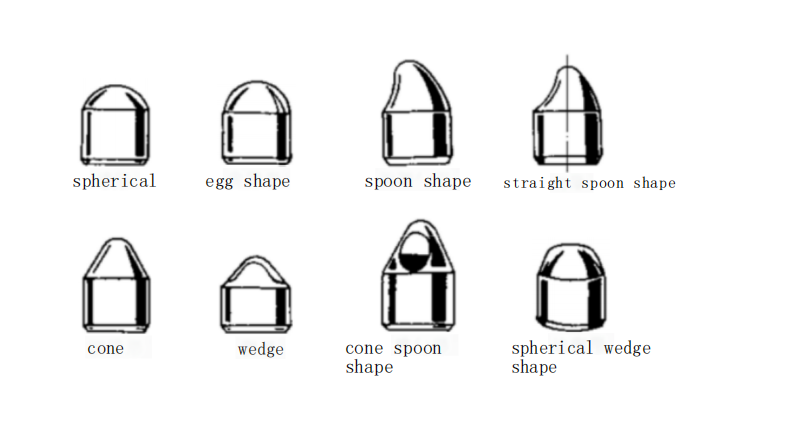
Wedge-shaped teeth
These teeth have a “wedge” shape, with tooth tip angles ranging from 65° to 90°. They are suitable for breaking highly plastic soft formations and moderately hard formations. Teeth with smaller tip angles are suitable for soft formations, while those with larger tip angles are suitable for harder formations.
Bucket-shaped teeth
Introduced in the 1980s by the Hughes Tool Company in the United States, this tooth shape is asymmetric and features a concave bucket-shaped cutting face and a slightly convex arc-shaped back. This structure improves tooth stress conditions, enhancing both crushing efficiency and tooth strength. It is effective for breaking very soft to moderately soft formation rocks.
Conical teeth
Conical teeth come in various shapes, including long cone, short cone, single cone, and double cone, with higher strength compared to wedge-shaped teeth. Medium conical teeth with angles of 60 to 70 degrees are used for drilling moderately hard formations such as limestone, dolomite, and sandstone. Teeth with 90° or 120° conical angles are used for drilling highly abrasive hard rocks like hard sandstone, quartzite, and flint.
Ball-shaped teeth
These teeth have a half-spherical top and are suitable for highly abrasive hard formations such as flint, quartzite, basalt, and granite. They offer both high strength and wear resistance.
???? ???????
?? ??? ??? ????? ????? ??????????.








