Casting
Liquid metal is poured into the cavity of the casting mold that is compatible with the shape and size of the part and left to cool and solidify to obtain a blank or part of the production method, usually called liquid metal forming or casting.
Process flow
liquid metal → filling → solidification and shrinkage → casting
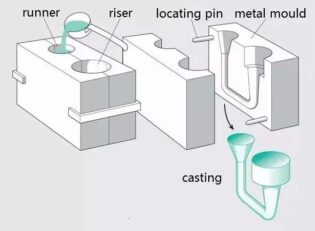
Process features.
1) It can produce parts with arbitrarily complex shapes, especially those with complex internal cavity shapes.
2) High adaptability, no restriction on alloy types and almost no restriction on casting size.
3)Wide source of materials, scrap can be remelted, low investment in equipment.
4)High scrap rate due to cracks, low surface quality and poor labor conditions.
Plastic forming
Plastic forming: It is the process of using the plasticity of the material to process the parts with less cutting or no cutting under the action of external force of tools and dies. It has many types, mainly including forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing, stamping, etc.
Forging
Forging is a processing method that uses forging machinery to apply pressure to metal billets to produce plastic deformation in order to obtain forgings with certain mechanical properties, certain shapes and sizes.
According to the forming mechanism, forging can be divided into free forging, die forging, lapping ring, special forging.
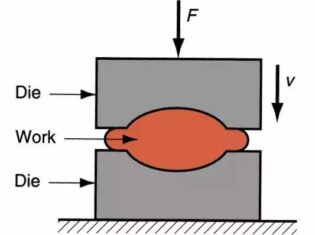
Free forging: Generally, it is the processing method to hammer the metal ingots or blocks into the required shape and size by using simple tools on the hammer forging or water press.
Die forging: It is formed by using dies on a die forging hammer or hot die forging press.
Ring lapping: refers to the production of ring-shaped parts of different diameters by special equipment ring lapping machine, also used to produce wheel-shaped parts such as automobile wheels and train wheels.
Special forging: including roll forging, wedge cross-rolling, radial forging, liquid die forging and other forging methods, these methods are more suitable for the production of certain special-shaped parts.
Process flow: forging billet heating → roll forging preparation → die forging forming → edge cutting → punching → correction → intermediate inspection → forging heat treatment → cleaning → correction → inspection
Technical characteristics.
(1) the quality of forgings than castings can withstand the effects of large impact, plasticity, toughness and other aspects of mechanical properties are also higher than castings or even higher than the rolled parts.
(2) save raw materials, but also shorten the processing time.
3) High production efficiency example.
4) Free forging is suitable for single-piece small batch production and is more flexible.
Applications.
Rollers and herringbone gears of large steel rolling mills, rotors, impellers and guard rings of turbine generator sets, working cylinders and columns of huge hydraulic presses, locomotive axles, crankshafts and connecting rods of automobiles and tractors, etc.
Rolling
Differing from forging, rolling makes the metal billet through the gap between a pair of rotating rolls (various shapes), due to the compression of the rolls forming rolling to reduce the material cross-section, the length of the pressure processing method increases.
Rolling classification.
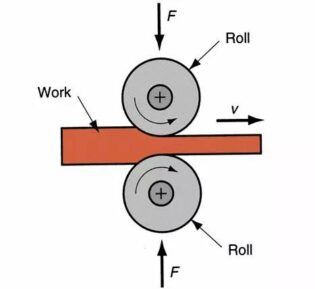
According to the movement of rolling parts are: longitudinal rolling, horizontal rolling, oblique rolling. Longitudinal rolling: is the metal in two rotational direction between the rolls through, and the process of plastic deformation in between.Cross-rolling: rolling deformation after the direction of movement and roll axis direction.Oblique rolling: rolled parts for spiral movement, rolled parts and roll axis non-special angle.
Applications
Mainly used in metal material profiles, plates, tubes, etc., and some non-metal materials such as plastic products and glass products.
Extrusion
Extrusion: The billet is extruded from the orifice or gap of the die under the action of uneven compressive stress in three directions so that the cross-sectional area is reduced and the length is increased to become the desired product processing method called extrusion, and this processing of the billet is called extrusion molding. 330mm long carbide rods are typical products made by using extrusion.
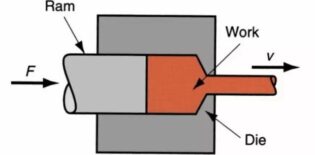
Process flow
Pre-extrusion preparation → casting bar heating → extrusion → stretching twisting straightening → sawing (sizing) → sampling inspection → artificial aging → packaging into storage
Advantages
1) Wide range of production, many product specifications and varieties.
2) High production flexibility, suitable for small batch production.
3) High dimensional accuracy and good surface quality of products.
4) Low investment in equipment, small plant area, easy to realize automatic production.
Disadvantages
1) large geometric waste loss.
2) Uneven metal flow.
3) low extrusion speed and long auxiliary time.
4) High tool loss and high cost.
Production scope of application: mainly used for manufacturing long rod, deep hole, thin wall, shaped section parts.
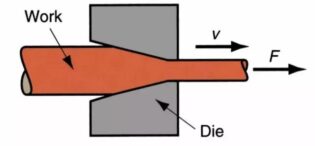
Drawing
Drawing: A plastic processing method in which a metal billet is pulled out from a die hole smaller than the billet section with an external force acting on the front end of the drawn metal to obtain a product of the corresponding shape and size.
Advantages
1) Accurate size and surface finish.
2) simple tools and equipment.
3) Continuous high-speed production of long products with small cross-sections.
Disadvantages
1) limited amount of deformation between passes and total deformation between annealing.
2)Length is limited.
Production range of application: drawing is the main processing method for metal pipes, bars, profiles and wires.
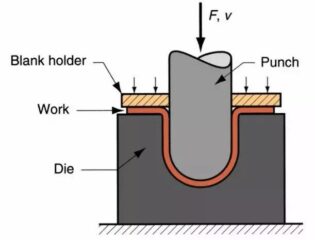
Stamping
Stamping: It is a forming process that relies on presses and dies to apply external forces to plates, strips, pipes and profiles to produce plastic deformation or separation to obtain workpieces (stampings) of the desired shape and size.
Technical characteristics.
1) Light weight and high rigidity products can be obtained.
(2) Good productivity, suitable for mass production and low cost.
(3) Uniform quality of products can be obtained.
(4) High material utilization, good shearability and recyclability.
Scope of application.
60-70% of the world’s steel is plate, most of which is made into finished products after stamping. The body, chassis, fuel tank and radiator sheet of automobile, steam ladle of boiler, shell of container, silicon steel sheet of iron core of motor and electric appliance are all stamping processed. There are also a large number of stamping parts in products such as instruments, household appliances, bicycles, office machinery, and living utensils.
Machining
Machining: is in the parts production process, directly with the tool in the blank to remove the excess metal layer thickness, so that it or the drawings required by the size accuracy, shape and location of mutual accuracy, surface quality, and other technical requirements of the processing process.
Commonly used machining methods are 1. Turning · 2. Drilling · 3. Milling · 4. Grinding · 5. Planing · 6. Sawing · 7. Broaching · 8. Electric Discharge Machining.
Welding
Also known as fusion welding, fusion welding is a manufacturing process and technique for joining metals or other thermoplastic materials such as plastics by means of heat, high temperature or pressure.
Powder metallurgy
It is the process technology to make metal or use metal powder (or mixture of metal powder and non-metal powder) as raw material, through forming and sintering, to manufacture metal materials, composite materials and various types of products. And tungsten carbide is made using this technology.
Advantages.
1) Most refractory metals and their compounds, pseudo-alloys, and porous materials can only be manufactured by powder metallurgy methods.
2) Save metal and reduce the cost of products.
3)Does not give the material any pollution, it is possible to make high purity material.
4)Powder metallurgy method can ensure the correctness and uniformity of material composition ratio.
5)Powder metallurgy is suitable for producing the same shape and a large number of products, which can greatly reduce the production cost.
Disadvantages.
1) In the absence of batch size to consider the size of the part.
2) The cost of the mold is relatively higher than the casting mold.
Production range of application.
Powder metallurgy technology can be directly made into porous, semi-dense or fully dense materials and products, such as oil-containing bearings, gears, cams, guide rods, tools, etc.
Metal Injection Molding
MIM (Metal injection Molding ): It is the abbreviation of metal injection molding. It is a molding method in which a plasticized mixture of metal powder and a binder is injected into a model. It is to mix the selected powder with the binder first, then granulate the mixture and inject it into the desired shape.
MIM process flow
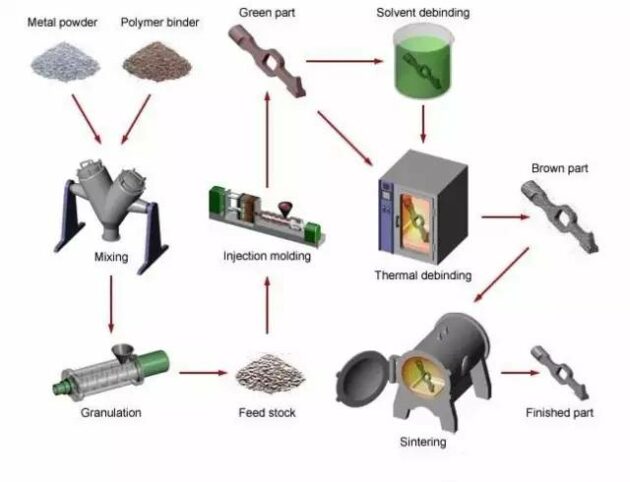
The MIM process is divided into four unique processing steps (mixing, molding, degreasing and sintering) to achieve the production of parts, and the need for surface treatment is determined by the product characteristics.
Technical features.
1) Forming responsible parts in one go.
2) Good surface quality of the manufactured part, low scrap rate, high production efficiency and easy automation.
3) Low requirements for mold materials.
Technology core.
Bonding agent is the core of MIM technology Only by adding a certain amount of bonding agent, the powder has enhanced fluidity to be suitable for injection molding and maintain the basic shape of the blanks.
Semi-Solid Metal Molding
Semi-Solid Molding: The unique rheology and churning properties of non-dendritic semi-solid metals (SSM) are used to control the quality of the casting. Semi-solid molding can be divided into rheological molding and thixotropic molding.
Technology features.
1) Reduction of liquid molding defects and significant improvement in quality and reliability.
2) lower molding temperature than all-liquid molding, which greatly reduces the thermal shock to the mold.
3) The ability to make alloys that are impossible to make by conventional liquid forming methods.
Applications.
It has been successfully used in the manufacture of master cylinders, steering system parts, rocker arms, engine pistons, wheel hubs, transmission system parts, fuel system parts and air conditioning parts, etc. in aviation, electronics as well as consumer products.
3D Printing
3D printing: A type of rapid prototyping technology, it is a technology that constructs objects by printing layer by layer using bondable materials such as powdered metal or plastic, based on digital model files.